作者:罂粟花
高剂量地塞米松用于接受全膝关节置换术的低疼痛反应患者:一项随机双盲试验

贵州医科大学 麻醉与心脏电生理课题组
翻译:胡廷菊 编辑:柏雪 审校:曹莹
背景:尽管采用了多模式镇痛,全膝关节置换术(TKA)的术后疼痛仍是一个持续存在的问题。研究表明,术前糖皮质激素的应用可以减少术后疼痛,但缺乏对特定患者的具体剂量和效果的研究。
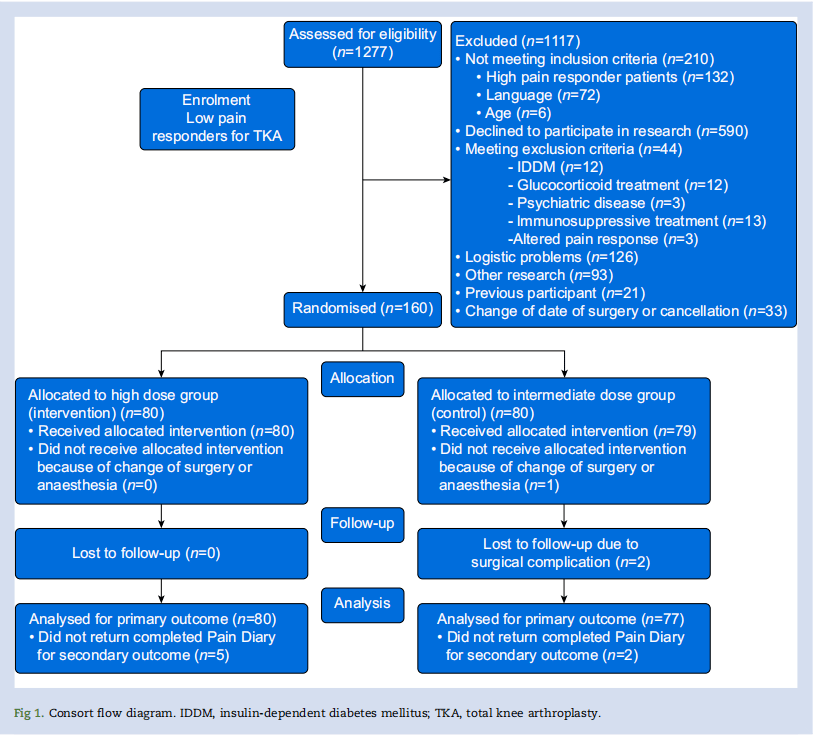
方法:一项双中心、双盲、双臂研究,160名拟行TKA手术,术前疼痛程度低且未使用阿片类药物的患者,观察术前使用地塞米松(1mg/kg vs 0.3mg/kg 静脉注射)对患者术后疼痛的影响。受试者采用了扑热息痛、环氧合酶-2抑制剂、局部麻醉浸润镇痛和补救性阿片类药物的多模式镇痛。主要结局是受试者术后24小时下床活动出现中度至重度疼痛(视觉模拟评分>30 mm)的百分比。次要结局包括疼痛评分、术后炎症(c反应蛋白)、阿片类药物和止吐药的使用、“恢复质量-15”和“阿片类药物相关症状困扰量表”、住院时间、再入院和90天内的并发症。
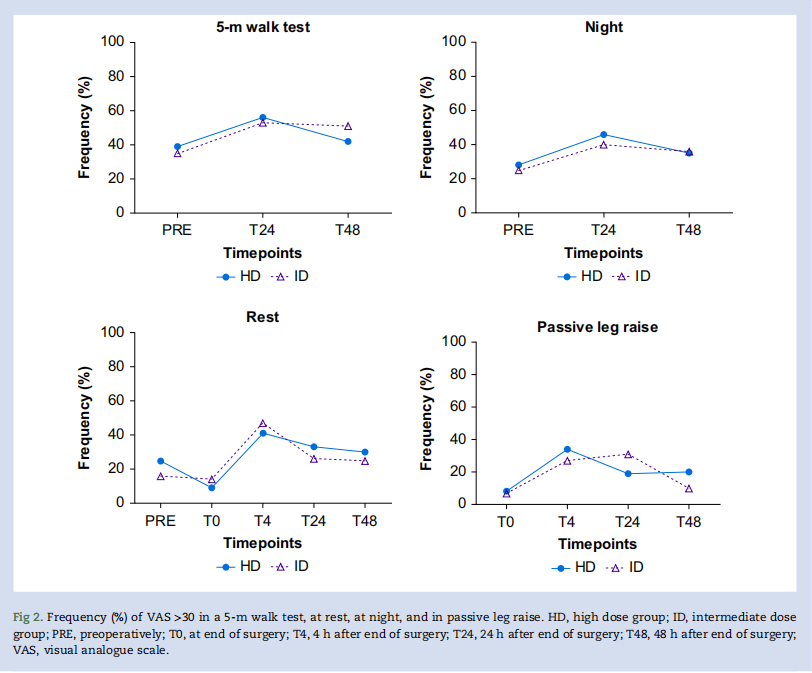
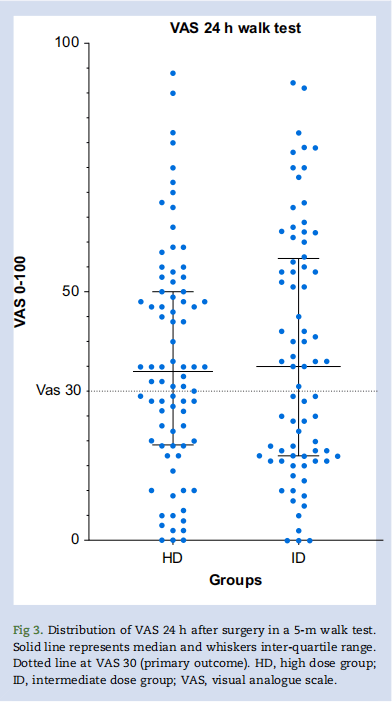
结果:共157名受试者(80 vs 77 ),受试者术后24小时下床活动时视觉模拟量表>30的发生率在两组间没有差异(56% vs 53%,相对风险=1.07,置信区间:0.8-1.4,P=0.65)。其他疼痛结局或补救性阿片类药物和止吐药的使用、恢复质量-15和阿片类药物相关症状困扰量表、住院时间、再入院和并发症无差异。C反应蛋白在24 小时时具有可比性(13 [6-25] mg/L vs 16 [9-38] mg/L,P=0.07),在48 小时时高剂量组较低(26 [9-52] mg/L vs 50 [30-72] mg/L,P<0.01)。



结论:使用1mg/kg vs 0.3mg/kg 地塞米松静脉注射,TKA后低疼痛反应人群与高疼痛反应人群相比,并没有改善术后早期疼痛或其他结局。
原始文献来源:Nielsen NI, Kehlet H, Gromov K, Troelsen A, Husted H, Varnum C, Kjærsgaard-Andersen P, Rasmussen LE, Pleckaitiene L, Foss NB. High-dose dexamethasone in low pain responders undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a randomised double-blind trial. Br J Anaesth. 2023 Mar;130(3):322-330. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2022.10.038. Epub 2022 Dec 14. PMID: 36526481.
英文原文:High-dose dexamethasone in low pain responders undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a randomised double-blind trial
Background:
Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a continuing problem despite optimised multimodal analgesia. Previous studies have shown preoperative glucocorticoids to reduce postoperative pain, but knowledge about specific doses and effects in specific patient groups is lacking.
Methods:A two-centre, double-blind, two-arm study comparing preoperative dexamethasone (1 mg/kg vs 0.3 mg /kg i.v.) on postoperative pain in 160 planned TKA subjects with low preoperative pain catastrophising and no opioid use. Subjects received multimodal analgesia with paracetamol, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, local anaesthetic infiltration analgesia, and rescue opioids. The primary outcome was percentage of subjects experiencing moderate to severe pain (visual analogue scale >30 mm) upon ambulation at 24 h. Secondary outcomes included pain scores, postoperative inflammation (C-reactive protein), opioid and antiemetics use, and ‘Quality of Recovery-15’ and ‘Opioid-Related Symptom Distress Scale’, length of stay, readmissions, and complications up to Day 90.
Results:A total of 157 subjects (80 vs 77) were included. No difference was found between groups in the incidence of subjects experiencing visual analogue scale >30 on ambulation 24 h after surgery (56% vs 53%, relative risk =1.07, confidence interval: 0.8-1.4, P=0.65). No differences in other pain outcomes or use of rescue opioids and antiemetics, in Quality of Recovery-15 and Opioid-Related Symptom Distress Scale, length of stay, readmissions, or complications. Creactive protein values were comparable at 24h (13 [6-25] mg/L vs 16 [9-38] mg/L , P =0.07), but lower at 48h (26 [9-52] mg/L vs 50 [30-72] mg/L , P<0.01) in the high-dose group.
Conclusions:Use of 1mg/kg vs 0.3mg/kg i.v. dexamethasone in low pain responders after TKA did not improve early postoperative pain or other outcomes in contrast to benefits in a high pain responder population.
END
本文转载自其他网站,不代表健康界观点和立场。如有内容和图片的著作权异议,请及时联系我们(邮箱:guikequan@hmkx.cn)
本文来自投稿,不代表长河网立场,转载请注明出处: http://www.changhe99.com/a/jmwx1qWbdN.html